

The viscosity of water at 20 degree celsius is approximately 1 milli pascal second. The SI unit of viscosity is pascal second. Example :- honey, egg white,oil, etc.The viscosity is generally denoted by 'eta'. To measure viscosity, fill a graduated cylinder with the liquid to be measured and mark the liquid's positions at the top and bottom of the cylinder. The vehicle owner’s handbook should always be consulted to determine the correct oil specifications for the vehicle. The viscosity of a fluid is due to the friction between the molecules of the fluid that are apparently moving in different speed. Oil with a viscosity that does not change much between the temperatures of 40c and 100c has a higher vi than an oil with a relatively higher change in viscosity. Increase fuel consumption and emissions.Older engines aren’t, so it’s important to always follow the manufacturer’s oil recommendations. Modern engines are designed to operate with low viscosity oils. ILSAC (International Lubricant Standardisation and Approval Committee).If a given lubricant’s viscosity is lower, it will. Kinematic viscosity is a fluid’s resistance to flow and shear due to gravity. To be more specific, there are two ways viscosity can be viewed: kinematic viscosity or dynamic viscosity. ACEA (Association des Constructeurs Europeens dAutomobiles) and Viscosity, in a general sense, is the measure of any liquid’s resistance to flow.You will see oil viscosity measurement in lube articles stated in kinematic (kv) and absolute (cSt) terms. Viscosity can be conceptualized as quantifying the internal frictional force that arises between adjacent layers of fluid that are in relative motion. For liquids, it corresponds to the informal concept of 'thickness': for example, syrup has a higher viscosity than water. The thicker (higher viscosity) of an oil, the slower it will flow. The viscosity of a fluid is a measure of its resistance to deformation at a given rate. However, producing oils with a low viscosity that provide the necessary engine protection and minimal oil consumption levels presents certain technical difficulties, and required the development of unique standards and service classifications for them. Simply put, viscosity is the oils resistance to flow or, for the layman, an oils speed of flow as measured through a device known as a viscometer. This takes less power from your engine, reduces fuel use, lowers exhaust emissions, and improves engine responsiveness.
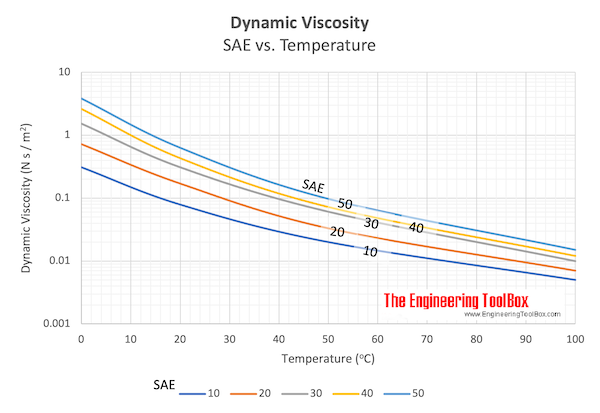
Most later engines are designed to use low viscosity engine oils to reduce internal drag. Production engines are increasingly moving to thinner, less viscous oil in search of improve fuel economy but there are performance advantages to thinner oil if the bearing clearances are somewhat tighter. The areas of application and possible uses of an oil are determined, among other. In simple terms, the word viscosity relates to a fluid’s resistance to flow. Viscosity is a rating system for oil that rates the oil’s thickness at a given temperature. Viscosity is one of the most important physical characteristics of a liquid.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
